
In 2024, Vietnam’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) landscape presents a dynamic and promising outlook, perfectly complementing its robust economic growth. With projections indicating a growth rate of around 5.8% in 2024, double the global average of 2.9%, Vietnam stands out as an enticing destination for foreign investors seeking lucrative opportunities. Given its strategic location in Southeast Asia and a rapidly expanding economy, Vietnam has captured significant interest from foreign investors across various sectors. This article explores the growth trends, assesses investment opportunities, and examines key drivers of Vietnam’s FDI, providing valuable insights for investors eyeing the Vietnamese market.
Growth Trends
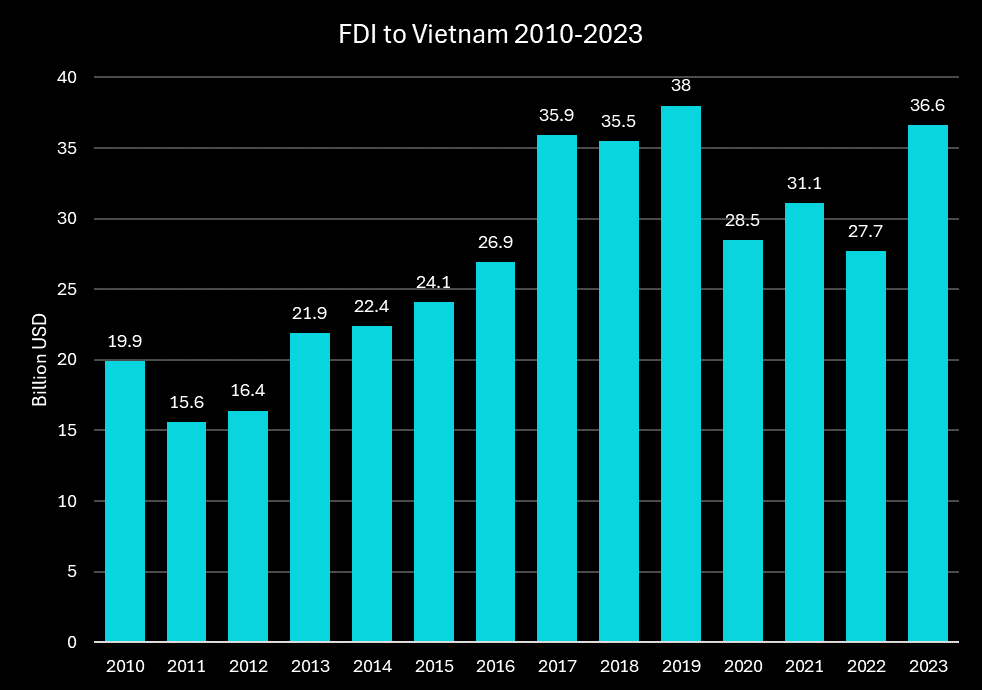
FDI inflow 2010-2023
Vietnam has experienced steady growth in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) over the past decade, peaking at $38 billion in 2019. Despite a drop during the COVID-19 pandemic, FDI rebounded to $36.61 billion by 2023. While EU investors fueled a 3% rise in global FDI in 2023, the Asia-Pacific region saw a 9% decline, with significant drops in China, India, and ASEAN countries. However, Vietnam, along with Thailand and Indonesia, defied this trend, with Vietnam recording a notable 32% increase in FDI in 2023.
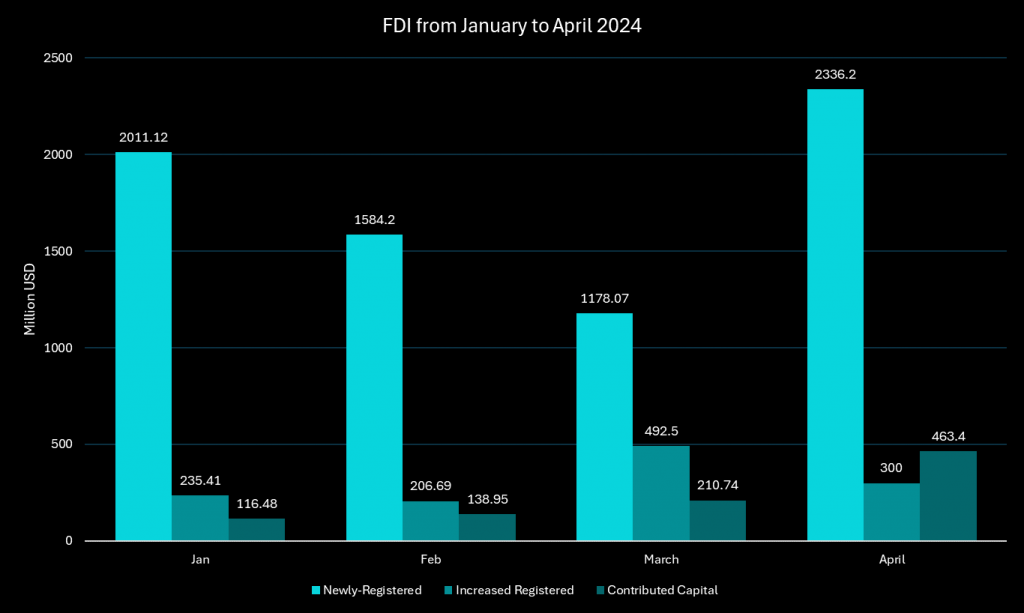
Vietnam’s FDI Surge in the First Four Months of 2024
In Q1 2024, Vietnam saw a 13.4% increase in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), with over $6.17 billion in newly registered and contributed capital from foreign investors. During the first four months of 2024, Vietnam issued investment certificates to 966 new projects, resulting in a 23.4% increase in project numbers and a 57.9% rise in capital value compared to the previous year. Additionally, $1.23 billion was allocated to expanding 345 existing projects, and $929.56 million was designated for stake purchases and capital contributions.
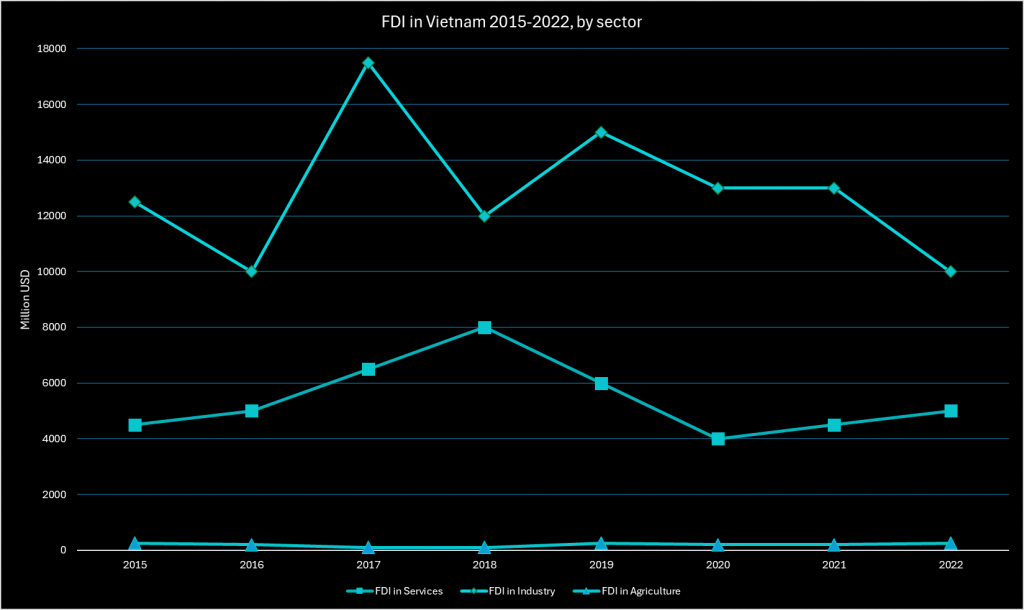
Key Invested Sectors
From 2015 to 2022, the Industry sector consistently attracted the most FDI, peaking at $17.25 billion in 2017 before declining to $9.41 billion by 2022. Despite the drop, Industry remained a primary investment focus. The opposite can be said for the Agriculture sector, consistently receiving the least FDI, with a peak of $179.3 million in 2017 but declining sharply to $30 million by 2022, reflecting higher perceived risks or lower potential returns compared to Services and Industry.
More specifically, over the past decade, manufacturing and real estate have been the top recipients of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), reflecting their pivotal roles in industrial growth and export competitiveness.
The Manufacturing and processing sector has consistently attracted the highest FDI, demonstrating a steady increase over the years. Starting from approximately $15,233 million in 2015, it reached nearly $30 billion by May 2024, highlighting its critical importance in driving industrial development and enhancing export capabilities.
The Real Estate sector: experienced notable fluctuations but maintained an overall upward trajectory. It saw a significant spike in 2018 and continued to grow, reaching $4,666 million by 2023. A 2.1 times YOY surge in the first four months of 2024 further indicates the sector’s resilience and potential for long-term investment returns.
Top sources of FDI in Vietnam
In 2023, Singapore led as the primary source of foreign investment, contributing a substantial $6.9 billion, which accounted for 18.6 percent of the total Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). This investment included 410 newly registered projects with a combined capital of $3,769 million. Additionally, Japan followed closely with $6.57 billion, including 302 newly registered projects worth $2.86 billion. Furthermore, mainland China and South Korea were significant contributors to Vietnam’s FDI landscape, especially South Korea contributed to the highest amount of increased registered capital at $2159 million during this period.
Investment Data for Top Investor Countries in 2023
In the first four months of 2024, Singapore, Hong Kong, Japan, South Korea, and mainland China continued to be major FDI sources. Singapore led with over $2.93 billion in total investment, including 138 newly registered projects worth $2.59 billion. Hong Kong ranked second with $1.05 billion, with 75.9% of its investment being new. Japan and China also had substantial newly registered investments, with Japan’s $814 million accounting for 85% and China’s $740 million accounting for 83.6% of their total investments. China led in the number of new projects, while South Korea excelled in capital adjustments and share purchases.
Investment Data for Top Investor Countries in Q1 2024
Key Catalysts for FDI’s Growth
Vietnam’s allure to Foreign Direct Investment stems from various factors. Let’s delve deeper into these pivotal drivers:
Geographical Positioning: Vietnam’s central location in Southeast Asia, with proximity to major economies and access to over 650 million people, along with its extensive coastline and deep-water ports, makes it a strategic entry point for businesses and a key player in global trade routes.
Growing Middle Class: Vietnam’s middle-income households are rapidly expanding, projected to comprise 30% of the population by 2026 and expected to grow by 36 million people by 2030. This growth positions Vietnam as an increasingly attractive consumer market with rising demand for higher value-added products and services.
Government Policies Favorable to Investors
The Vietnamese government offers a range of incentives to attract foreign direct investment. These incentives are designed to align with national development strategies and support economic growth
Corporate Income Tax (CIT) Incentives: Preferential tax rates of 10% or 17% for the lifetime of a project or for 10-15 years, and tax holidays with full exemptions for 2-4 years, followed by a 50% tax reduction for 4-9 years.
Economic Zone Incentives: Enhanced infrastructure and tax benefits in economic zones, including tax holidays and preferential CIT rates, with up to a 10% CIT rate for the project’s lifetime in extremely disadvantaged areas.
Industrial zones
Vietnam’s three key economic zones—NKEZ (Northern), CKEZ (Central), and SKEZ (Southern)—attract investors with their specialized industries and strategic locations. The NKEZ, including Hanoi and Hai Phong, focuses on electronics, motorcycles, and high-tech manufacturing. The CKEZ, centered around Da Nang, specializes in light industries like food processing and apparel. The SKEZ, anchored by Ho Chi Minh City, is a hub for rubber, plastics, apparel, machinery, and metallurgy, making it particularly appealing to small and medium-sized manufacturers.
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
Vietnam has engaged in 18 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), both bilateral (with Japan, Chile, South Korea, the EU, UK, etc.) and multilateral (within ASEAN, CPTPP, and RCEP). Additionally, it maintains Comprehensive Strategic Partnerships with 7 countries, including Russia, China, India, and the US. These agreements enhance Vietnam’s trade competitiveness by reducing tariffs and diversifying sourcing, boosting FDI, and facilitating the transition from low-tech to high-tech exports. They also improve product quality, labor rights, and environmental protections, making Vietnam an attractive destination for foreign investors.
Anticipated Trends Shaping FDI in Vietnam
Healthcare Growth: Vietnam’s healthcare sector is expanding rapidly due to a growing middle class and aging population. The pharmaceutical market is expected to reach over $10 billion by 2026, with significant opportunities in pharmaceutical production, specialized hospitals, and medical tourism, which currently account for 300,000 foreign visitors each year.
Renewable Energy Shift: In order to navigate the challenge to balance between its burgeoning energy demands and environmental sustainability, Vietnam is increasing its focus on renewable energy, aiming to have renewables make up 30.9-39.2% of its energy mix by 2030, and 67.7-71.5% by 2050. This shift presents substantial investment opportunities, particularly in solar, wind, biomass, and ammonia.
Technology and Software Development: Vietnam is a hub for software development, with over 530,000 skilled developers and 50,000 IT graduates every year along with competitive labor costs and. Coupled with the country’s proficiency in AI, blockchain, and IoT, Vietnam is surely an attractive destination for foreign tech firms.
Electronics Manufacturing Hub: Vietnam’s strategic location and robust manufacturing base have attracted major electronics companies like Samsung, LG, and Foxconn, with electronics exports reaching $78.5 billion in 2023.
Conclusion
Vietnam has shown consistent FDI growth, with a strong recovery post-COVID-19. In early 2024, 966 new projects were launched, particularly in manufacturing, real estate, and technology. Fueled by its strategic location, growing middle class, favorable policies, and infrastructure investments, the future holds lots of opportunities for the new super star, especially in healthcare, renewable energy, and technology, highlighting Vietnam’s commitment to sustainable development and its appeal as a top FDI destination.
If you are a foreign investor aiming to join in on the FDI trend of Vietnam, several key guidelines should be considered. We recommend familiarizing yourself with local regulations and business practices, engaging in thorough market research to understand consumer preferences and industry dynamics, and cultivating strong relationships with local partners and stakeholders to navigate the business landscape effectively. With CCX Partner’s extensive experience, strategic insights, and locally-global approach, we empower businesses to navigate complexities and seize opportunities in the Vietnamese market. Let CCX Partners be your guide on the journey to success in Vietnam’s thriving manufacturing landscape.